1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
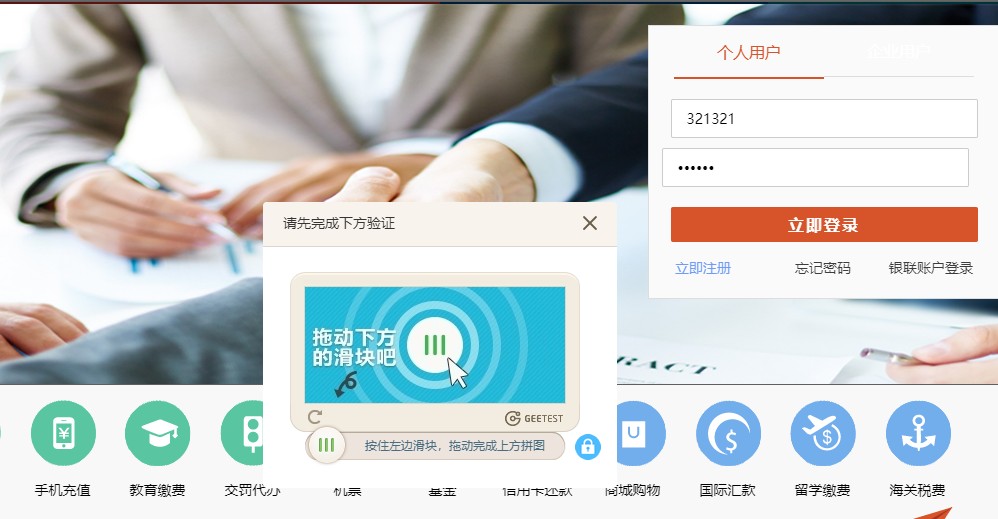
| import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import requests
from io import BytesIO
class CaptchaProcessor:
def __init__(self):
self.image_cache = {}
self.template_cache = {}
def download_image(self, url):
"""下载验证码图片"""
response = requests.get(url)
image = Image.open(BytesIO(response.content))
return cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
def preprocess_image(self, image):
"""图像预处理"""
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
edges = cv2.Canny(blurred, 50, 150)
return edges
def find_template_match(self, background, template):
"""模板匹配寻找缺口位置"""
result = cv2.matchTemplate(background, template, cv2.TM_CCOEFF_NORMED)
_, max_val, _, max_loc = cv2.minMaxLoc(result)
if max_val > 0.6:
return max_loc
else:
return None
def detect_gap_position(self, background_path, slider_path):
"""检测缺口位置"""
background = cv2.imread(background_path)
slider = cv2.imread(slider_path)
bg_processed = self.preprocess_image(background)
slider_processed = self.preprocess_image(slider)
gap_position = self.find_template_match(bg_processed, slider_processed)
if gap_position:
return {
'x': gap_position[0],
'y': gap_position[1],
'confidence': 0.85,
'method': 'template_matching'
}
else:
return self.detect_gap_by_edges(background)
def detect_gap_by_edges(self, image):
"""基于边缘检测的缺口识别"""
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 150)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(edges, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
if 50 < area < 5000 and 20 < w < 100 and 20 < h < 100:
return {
'x': x,
'y': y,
'width': w,
'height': h,
'method': 'edge_detection'
}
return None
|